Evaluation and Assessment of the Indonesian Language in Elementary Schools: Language Content Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.56630/mes.v3i2.228Keywords:
Evaluation and Assessment, Indonesian Language , Elementary School , Language Content AnalysisAbstract
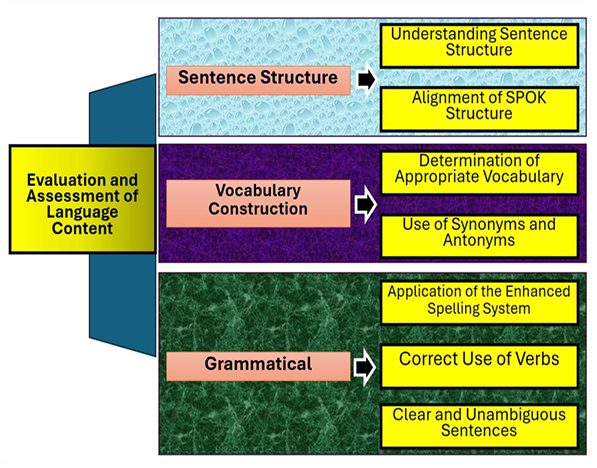
Evaluation and assessment are an important part of teaching, aiming to measure students' understanding and monitor their progress in children's language learning. This study examines the purpose and function of evaluation carried out by teachers in monitoring student progress, especially in the context of the content structure and language vocabulary used by students in elementary schools. The method used is language content analysis, focusing on daily tasks involving the preparation of sentence structure and vocabulary selection. The subject of the research is grade V students at UPT SPF SD Inpres Tamalanrea 5 Makassar, with a qualitative approach. The results of the study show that evaluation plays a role not only in providing information about student progress, but also as a tool to improve the quality of learning and encourage students and teachers to continue to improve the learning process for better achievement of goals. The contribution of this research is to provide insight into how evaluation based on sentence structure analysis, vocabulary construction, and grammatical stimulates the improvement of students' language skills in elementary school, as well as provide a deeper understanding of how evaluation can be optimally integrated in learning activities to encourage the development of students' language skills.
References
Ahmed Alismail, H. (2023). Teachers’ perspectives of utilizing distance learning to support 21st century skill attainment for K-3 elementary students during the COVID-19 pandemic era. Heliyon, 9(9), e19275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19275
Al-Akbari, S., Nikolov, M., & Hódi, Á. (2024). EFL teachers’ language assessment literacy training needs. Social Sciences & Humanities Open, 11(3), 5265–5288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssaho.2024.101254
Andreani, W., & Ying, Y. (2019). “PowPow” interactive game in supporting English vocabulary learning for elementary students. Procedia Computer Science, 473–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.09.005
Ardasheva, Y., Carbonneau, K. J., Roo, A. K., & Wang, Z. (2018). Relationships among prior learning, anxiety, self-efficacy, and science vocabulary learning of middle school students with varied English language proficiency. Learning and Individual Differences, 61(1), 21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2017.11.008
Arman, A. A., N, A. B. P., Purwarianti, A., & Kuspriyanto. (2013). Syntactic phrase chunking for Indonesian language. Procedia Technology, 635–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2013.12.239
Barnes-Holmes, Y., Barnes-Holmes, D., & Murphy, C. (2004). Chapter 16 - Teaching the generic skills of language and cognition: contributions from relational frame theory. In Evidence-Based Educational Methods (pp. 277–293). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-012506041-7/50017-6
Busse, V., Hennies, C., Kreutz, G., & Roden, I. (2021). Learning grammar through singing? An intervention with EFL primary school learners. Learning and Instruction, 71(2), 425–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2020.101372
Cakiroglu, A., & Kuruyer, H. G. (2021). First grade Elementary School Student’s Family Involvement in the Process of Reading and Writing Skills Acquisition. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 5588–5592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.06.480
Chowdhury, M., Dixon, L., Kuo, L.-J., Donaldson, J. P., Eslami, Z., Viruru, R., & Luo, W. (2024). Digital game-based language learning for vocabulary development. Computers and Education Open, 6(2), 627–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeo.2024.100160
Cockerill, M., Roseth, C., & O’Keeffe, J. (2024). A Phase 3 randomized controlled trial of a vocabulary program in elementary schools in England: Protocol. International Journal of Educational Research, 128(1), 193–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2024.102448
Folse, K. (2023). Teaching academic writing: practical techniques in vocabulary and grammar. Journal of Second Language Writing, 61(1), 15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jslw.2023.101036
Gonzalez, J. E., Kim, H., Anderson, J., & Pollard-Durodola, S. (2024). The Effects of a Science and Social Studies Content Rich Shared Reading Intervention on the Vocabulary Learning of Preschool Dual Language Learners. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 66(1), 34–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecresq.2023.08.011
Hernández-Ocampo, S. P., Chala-Bejarano, P. A., & Rodríguez-Uribe, M. (2024). Pre-service english teachers’ perceptions of language assessment in a colombian language teacher education program. International Journal of Educational Research Open, 8(2), 326–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijedro.2024.100405
Huang, C.-Y., & Wang, J. C. (2022). Effectiveness of a three-dimensional-printing curriculum: Developing and evaluating an elementary school design-oriented model course. Computers & Education, 187(2), 163–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2022.104553
Jo, J., Sundara, M., & Breiss, C. (2024). Predicting language outcomes at 3 years using individual differences in morphological segmentation in infancy. Infant Behavior and Development, 77(1), 53–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infbeh.2024.102001
Johnson, E., Atkinson, P., Muggeridge, A., Cross, J. H., & Reilly, C. (2022). Impact of epilepsy on learning and behaviour and needed supports: Views of children, parents and school staff. European Journal of Paediatric Neurology, 40(1), 61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpn.2022.08.001
Kain, C., Koschmieder, C., Matischek-Jauk, M., & Bergner, S. (2024). Mapping the landscape: A scoping review of 21st century skills literature in secondary education. Teaching and Teacher Education, 151(1), 48–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2024.104739
Kelley, E. S., Peters-Sanders, L., Sanders, H., Madsen, K., Seven, Y., & Goldstein, H. (2024). Dynamic assessment of word learning as a predictor of response to vocabulary intervention. Journal of Communication Disorders, 113(2), 321–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcomdis.2024.106478
Koivuhovi, S., Kilpi-Jakonen, E., Erola, J., & Vainikainen, M.-P. (2024). Parental involvement in elementary schools and children’s academic achievement: A longitudinal analysis across educational groups in Finland. Research in Social Stratification and Mobility, 95(1), 42–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rssm.2024.101007
Kralova, Z., Kamenicka, J., & Tirpakova, A. (2022). Positive emotional stimuli in teaching foreign language vocabulary. System, 104(2), 527–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.system.2021.102678
Kwangmuang, P., Jarutkamolpong, S., Duangngern, P., Gessala, N., & Sarakan, P. (2024). Promoting analytical thinking skills development in elementary school students through animated cartoons. Computers in Human Behavior Reports, 15(1), 48–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chbr.2024.100467
Lanauze, M., & Snow, C. (2023). The relation between first-and second-language writing skills: Evidence from Puerto Rican elementary school children in bilingual programs. Linguistics and Education, 4(1), 77–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0898-5898(89)80005-1
Liao, W., Li, X., Dong, Q., & Wang, Z. (2023). Non-university-based teacher educators’ professional learning: A systematic review. Teaching and Teacher Education, 136(2), 354–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2023.104374
Lidice, A., & Saglam, G. (2013). Using students’ evaluations to measure educational quality. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 1009–1015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.01.152
Lin, L.-F. (2015). The impact of problem-based learning on Chinese-speaking elementary school students’ English vocabulary learning and use. System, 55(1), 173–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.system.2015.08.004
Liu, Y., Xu, G., Yuan, S., Zhou, C., & Wang, C. (2024). Assessment as learning: Evidence based on meta-analysis and quantitative ethnography research. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 83(1), 125–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stueduc.2024.101423
Ma, X., Zhou, Q., & Li, Y. (2024). Multi-interest sequential recommendation with contrastive learning and temporal analysis. Knowledge-Based Systems, 305(3), 6356–6378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2024.112657
Moiseenko, L. (2014). Formation of the prerequisites of writing skills in preschool childhood with the help of specially organized multifunctional subject-developing environment. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 470–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.08.157
Morgan, P. L., Farkas, G., Oh, Y., & Hillemeier, M. M. (2024). Executive functions, oral vocabularies, and early literacy skills mediate sociodemographic gaps in mathematics and science achievement during elementary school. Learning and Individual Differences, 112(2), 539–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2024.102447
Poláková, P. (2022). Use of a mobile learning application in the process of foreign vocabulary learning. Procedia Computer Science, 64–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2022.09.038
Rimmer, C., Dahary, H., & Quintin, E.-M. (2022). Emergent literacy skills and autism: A scoping review of intervention programs. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 97(2), 456–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2022.102004
Shahiwala, S., Rahul, D. R., & Baker, J. R. (2024). Incidental vocabulary learning: A scientometric review. Research Methods in Applied Linguistics, 3(3), 6376–6390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmal.2024.100160
Sharifi, M., Azizifar, A., Jamalinesari, A., & Gowhary, H. (2015). The effect of rosetta stone computer software on vocabulary learning of Iranian elementary EFL learners. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 260–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.06.037
Silverman, R. D., Artzi, L., McNeish, D. M., Hartranft, A. M., Martin-Beltran, M., & Peercy, M. (2019). The relationship between media type and vocabulary learning in a cross age peer-learning program for linguistically diverse elementary school students. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 56(1), 106–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2018.12.004
Su-Chiao, & Yu-Liang. (2015). Advancing kindergarten teachers’ knowledge and capabilities of differentiated instruction associated with implementation of thematic integrated curriculum. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 246–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.02.404
Sugaya, A., Fukushima, K., Takao, S., Kasai, N., Maeda, Y., Fujiyoshi, A., Kataoka, Y., Kariya, S., & Nishizaki, K. (2019). Impact of reading and writing skills on academic achievement among school-aged hearing-impaired children. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology, 126(2), 1532–1547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.109619
Teng, M. F. (2024). Working memory and prior vocabulary knowledge in incidental vocabulary learning from listening, reading, reading-while-listening, and viewing captioned videos. System, 124(1), 537–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.system.2024.103381
Thompson, J., & Childers, G. (2021). The impact of learning to code on elementary students’ writing skills. Computers & Education, 175(1), 73–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2021.104336
Troia, G. A., Wang, H., & Lawrence, F. R. (2022). Latent profiles of writing-related skills, knowledge, and motivation for elementary students and their relations to writing performance across multiple genres. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 71(1), 300–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2022.102100
Yıldırım, B., & Topkaya, E. Z. (2020). Clarificative evaluation of elementary level grammar program of a tertiary level preparatory class in Turkey. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 65(1), 62–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stueduc.2020.100862
Zhang, Z., Li, H., & Zhou, J. (2023). Teaching with social context in instructional video facilitates second language vocabulary learning. Heliyon, 9(3), 547–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14540
Zheng, Z., Wu, X., & Liu, X. (2024). Enhancing pre-trained language models with Chinese character morphological knowledge. Information Processing & Management, 62(1), 84–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2024.103945
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Andi Erwin Ali Cappa & Rahma Ashari Hamzah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with Journal of Madako Elementary School agree to the following terms:
- For all articles published in the Journal of Madako Elementary School, copyright is retained by the authors. Authors give permission to the publisher to announce the work with conditions. When the manuscript is accepted for publication, the authors agree to the automatic transfer of non-exclusive publishing rights to the publisher.
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).



.png)
.png)












